How to test the performance for the code in C# ?
In this blog, we will learn how to
test the performance of the C# code. For the performance, we will use
benchmarking.
Benchmark
Benchmarking measures how well a piece of code
performs; it evaluates the code and aids in performance improvement. We
utilized the Benchmarkdotnet package to carry out the
benchmarking in C#.
BenchmarkDotNet
BenchmarkDotNet is a nice tool
that provides a simple way to make an informed decision about the performance
metrics of your application. In BenchmarkDotNet, the invocation of a method
that has the Benchmark attribute set is known as an operation. An iteration is
the name given to a collection of several operations.
A small, effective, open-source.NET framework
called BenchmarkDotNet may turn your processes into benchmarks, monitor their
effectiveness, and share reproducible measurement tests. It isn't more
difficult than writing unit tests.
In this project, there are two methods we must use to call an API: one is
Httpwebrequest and the other is Rest Sharp.
We have therefore contrasted these's performances using the benchmark.
To begin,
we build an Asp.net Core MVC project. Next, we visit the Package Manager
Console.
add the benchmark NuGet package
Steps for benchmarking code using BenchmarkDotNet
To run BenchmarkDotNet in your .NET Framework or .NET Core application
you must follow these steps:
1.
Add the necessary NuGet package
2.
Add Benchmark attributes to your methods
3.
Create a BenchmarkRunner instance
4.
Run the application in Release mode
Create a benchmarking class in .NET Core
Open the Program.cs file and write the following
code in there.
[MemoryDiagnoser]
public class MemoryBenchmarkerDemo
{
int NumberOfItems = 100000;
[Benchmark]
public string ConcatStringsUsingStringBuilder()
{
var sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < NumberOfItems; i++)
{
sb.Append("Hello World!" + i);
}
return sb.ToString();
}
[Benchmark]
public string ConcatStringsUsingGenericList()
{
var list = new List<string>(NumberOfItems);
for (int i = 0; i < NumberOfItems; i++)
{
list.Add("Hello World!" + i);
}
return list.ToString();
}
}
In the Main method of the Program.cs file you must
specify the initial starting point — the BenchmarkRunner class.
Run the benchmark in your .NET Core application
Running benchmark code in debug mode will result in an error.
Hence you should run your project in the release
mode only. To run benchmarking, specify the following command at the Visual
Studio command prompt.
dotnet run -p BenchmarkDotNetDemo.csproj -c Release
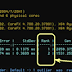
When you run this command, the
benchmarking process kicks off and displays the output after the benchmarking
process has been executed successfully



No comments